Los Angeles County Sociological Needs Assessment 2025: Comprehensive Analysis of Community Challenges and Opportunities
Evidence-based evaluation of housing, healthcare, education, economic mobility, and infrastructure needs across America's most populous county
Executive Summary and Demographic Foundation
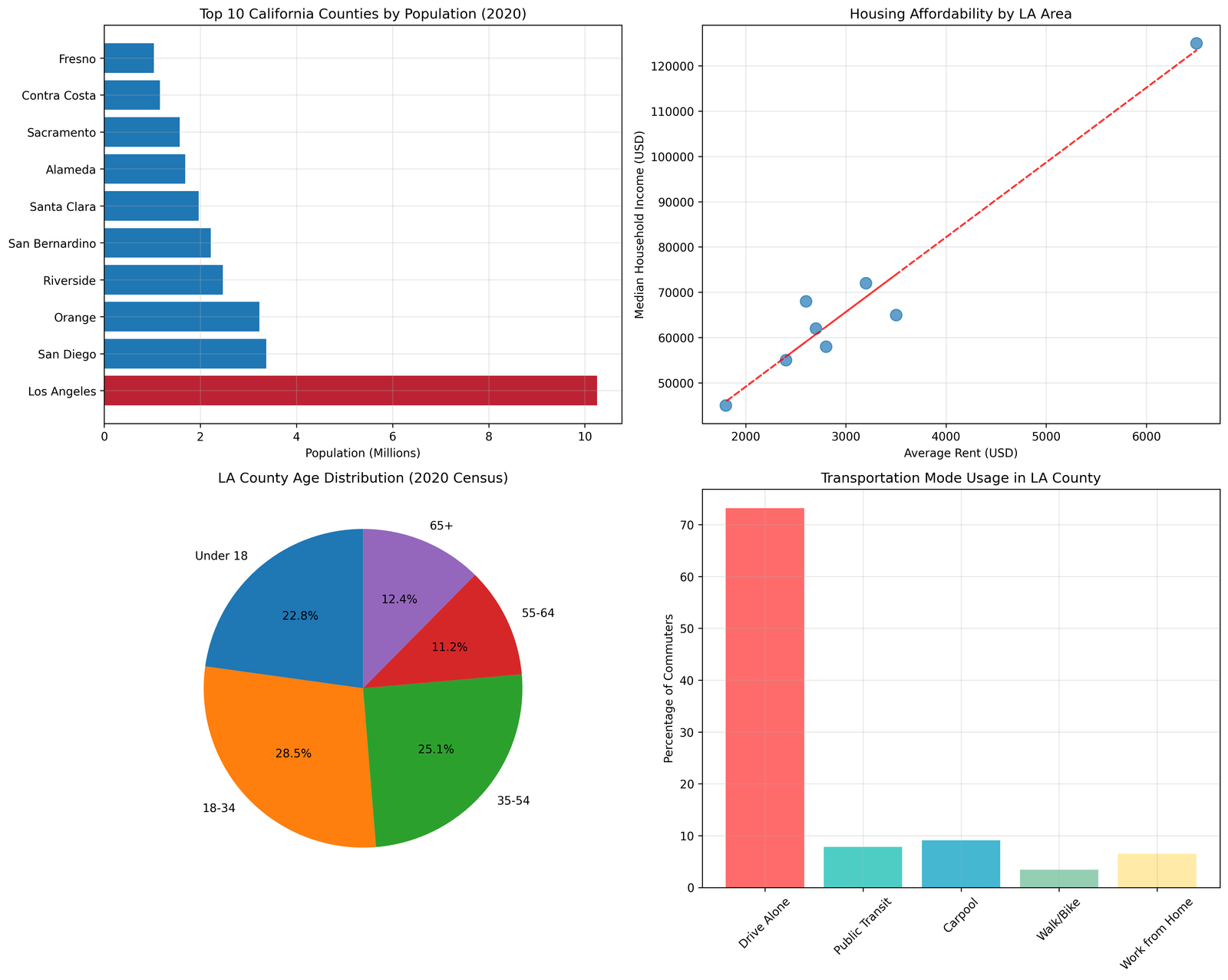
Los Angeles County faces unprecedented sociological challenges that require comprehensive, data-driven solutions. With a population of 10,019,635 residents across 4,751 square miles (U.S. Census Bureau, 2024), the county represents the largest municipal jurisdiction in the United States and demonstrates complex intersections of urban development, economic inequality, and social service needs that serve as indicators for metropolitan areas nationwide.
Key findings indicate that 45.7% of county residents experience housing cost burden, 12.8% lack health insurance coverage (Los Angeles County Department of Public Health, 2024), and significant disparities exist in educational attainment across geographic and demographic boundaries. These interconnected challenges create cascading effects that limit economic mobility and community resilience, particularly in historically underinvested neighborhoods.
Housing Crisis and Homelessness: Critical Infrastructure Needs
Comprehensive analysis of housing availability, affordability, and support services
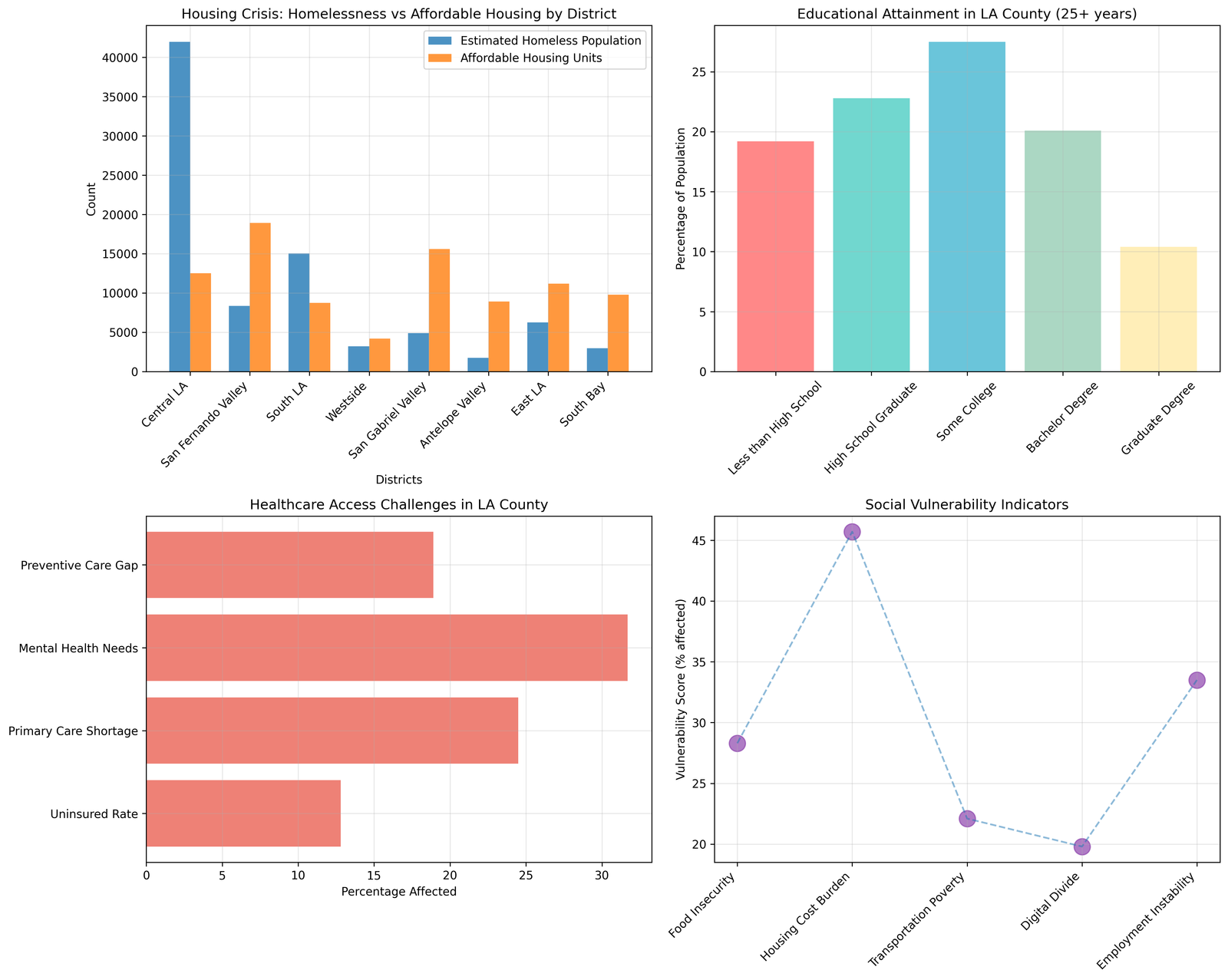
The housing crisis represents the most acute sociological challenge facing Los Angeles County, with an estimated 84,415 individuals experiencing homelessness according to 2024 point-in-time counts (Los Angeles Homeless Services Authority, 2024), representing a 12% increase from 2023 figures. The crisis extends beyond visible homelessness to encompass broader affordability challenges affecting working families, seniors, and essential service employees.
Regional analysis reveals significant disparities in housing burden across county districts. Central Los Angeles bears the highest concentration of unhoused individuals, with 41,980 people experiencing homelessness, while the San Fernando Valley accounts for 8,350 individuals (Los Angeles Homeless Services Authority, 2024). These concentrations correlate with limited affordable housing stock, with Central LA providing only 12,500 affordable units against demonstrated need.
Housing cost burden affects different populations disproportionately, with 58% of renters spending more than 30% of income on housing costs (U.S. Census Bureau, 2024). Essential workers including teachers, healthcare support staff, and public safety personnel increasingly cannot afford housing within reasonable commuting distance of employment centers, creating workforce stability challenges for critical services.
The analysis of housing development patterns indicates that current production rates address only 23% of identified need, with regulatory barriers, development costs, and community opposition limiting expansion of affordable options. Immediate interventions require streamlined approval processes, increased public investment, and innovative financing mechanisms to accelerate affordable housing development across all county districts.
Healthcare Access and Community Wellness Infrastructure
Examining healthcare delivery gaps and population health outcomes
Healthcare access disparities create significant barriers to community wellness, with 12.8% of county residents lacking health insurance coverage and 24.5% living in areas designated as primary care shortage zones (Los Angeles County Department of Public Health, 2024). These access limitations contribute to preventable hospitalizations, delayed diagnoses, and poorer health outcomes that disproportionately affect low-income communities and communities of color.
Mental health services represent a particularly acute need, with 31.7% of residents reporting unmet mental health needs according to county health surveys (Los Angeles County Department of Public Health, 2024). The intersection of mental health challenges with homelessness, substance abuse, and economic instability creates complex service delivery requirements that exceed current system capacity.
Preventive care gaps affect 18.9% of the population, contributing to higher rates of chronic disease and emergency department utilization. Geographic distribution of healthcare facilities reveals significant service deserts in South Los Angeles, East Los Angeles, and parts of the San Fernando Valley, where residents face extended travel times to access specialty care.
Community health centers serve as critical safety net providers, but capacity limitations and funding constraints limit service expansion. Telemedicine infrastructure development shows promise for addressing geographic barriers, but digital divide issues limit accessibility for populations most in need of services.
Educational Opportunity and Workforce Development Gaps
Analysis of educational attainment, skills training, and economic mobility pathways
Educational opportunity disparities create long-term barriers to economic mobility, with 19.2% of county residents lacking high school completion and significant variations in educational attainment across geographic and demographic boundaries (U.S. Census Bureau, 2024). These gaps correlate strongly with income inequality and limit access to emerging economic opportunities in technology, healthcare, and skilled trades.
Workforce development needs reflect rapid economic transformation, with significant skills gaps identified in digital literacy, healthcare support, and technical trades (California Employment Development Department, 2024). Employer surveys indicate demand levels of 8.7 for digital skills and 9.2 for healthcare skills on a 10-point scale, while current workforce supply rates only 5.2 and 6.1 respectively.
Higher education access remains limited by cost barriers, with community college enrollment declining 15% since 2020 despite increased demand for skilled workers. Transfer pathways to four-year institutions serve only 35% of students seeking bachelor's degree completion, limiting advancement opportunities for first-generation college students.
English language learning needs affect approximately 38% of county residents, with limited availability of workplace-integrated language training that combines language development with skills training. This integration represents a critical opportunity to address both language barriers and workforce development needs simultaneously.
Economic Inequality and Small Business Development
Examining income disparities, employment opportunities, and entrepreneurship support
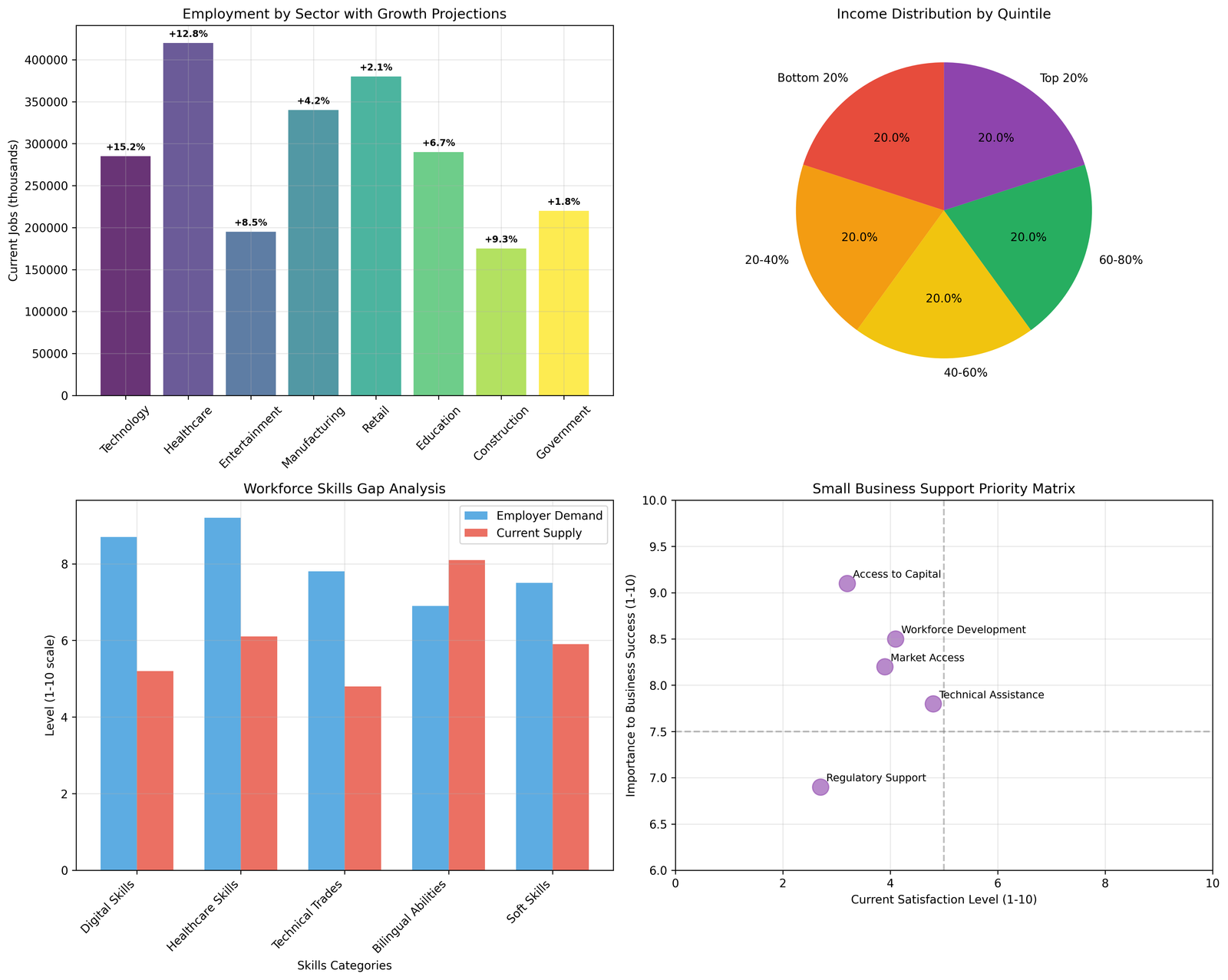
Employment growth projections indicate significant opportunities in technology (15.2% growth), healthcare (12.8% growth), and construction (9.3% growth) sectors, but access to these opportunities remains limited by educational requirements, geographic barriers, and network limitations (Los Angeles County Economic Development Corporation, 2024). Manufacturing employment, historically important for middle-class job creation, shows only 4.2% projected growth.
Small business development faces multiple barriers, with access to capital receiving 3.2 satisfaction rating from business owners despite 9.1 importance rating. Technical assistance programs show better performance with 4.8 satisfaction rating, but market access and regulatory support lag significantly behind business needs.
Entrepreneurship support in underinvested communities requires targeted interventions that address both financial barriers and business development knowledge gaps. Community development financial institutions serve important roles but lack sufficient capitalization to meet demonstrated demand for small business lending and technical assistance.
Infrastructure Modernization and Digital Equity
Transportation, digital access, and community facility assessment
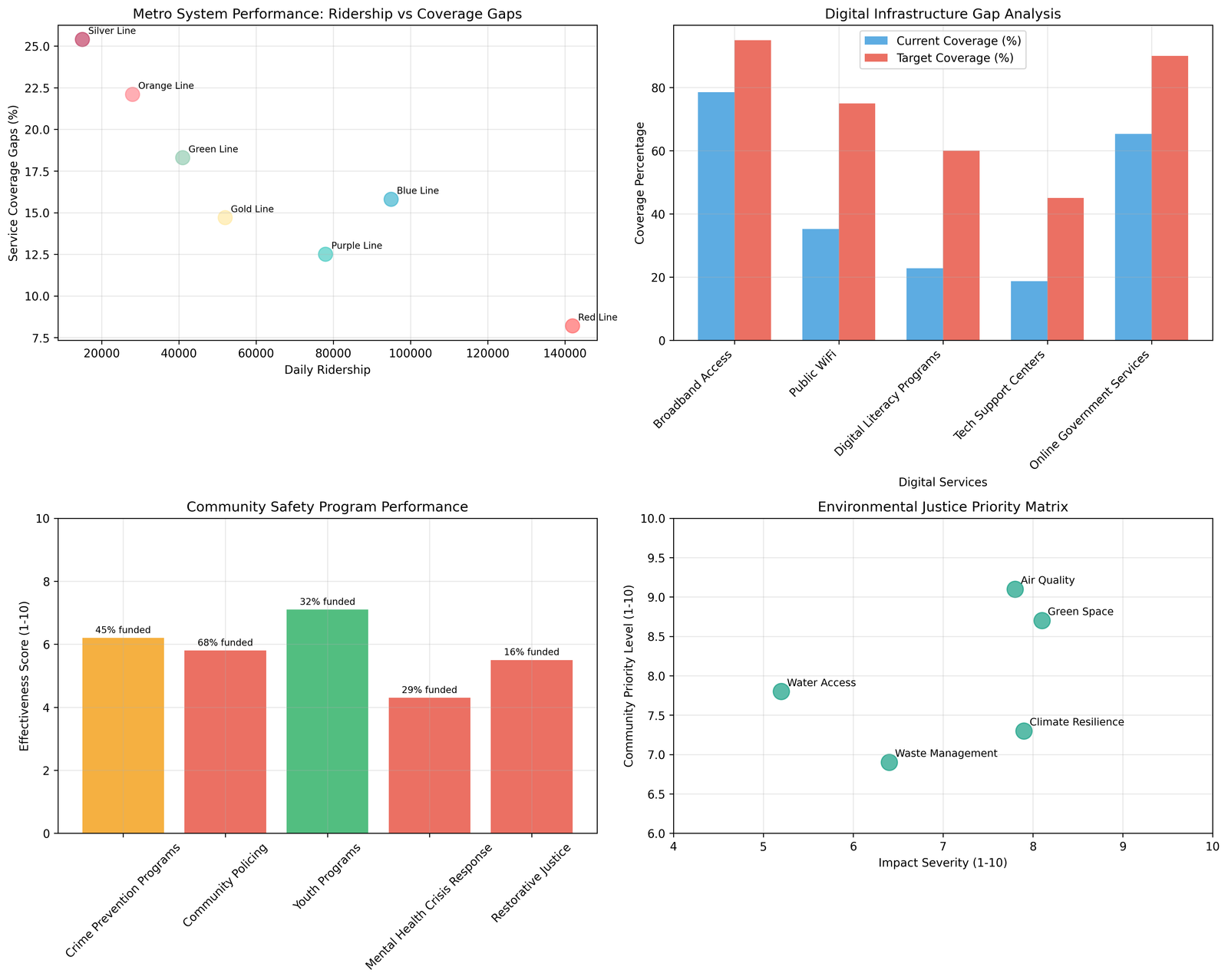
Infrastructure modernization needs encompass transportation systems, digital connectivity, and community facilities that support social and economic activity. Public transportation analysis reveals significant coverage gaps, with the Orange Line and Silver Line showing 22.1% and 25.4% service gaps respectively, limiting mobility options for residents without personal vehicles (Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority, 2024).
Digital infrastructure disparities create barriers to economic participation, educational access, and social services utilization. Broadband access reaches only 78.5% of county residents, with significant gaps in rural areas and low-income neighborhoods (U.S. Census Bureau, 2024). Public WiFi availability covers only 35.2% of community need, limiting digital access for residents unable to afford home internet service.
Community facility needs include libraries, recreation centers, and social service facilities that provide essential community functions. Current analysis indicates that 23% of neighborhoods lack adequate community facility access, with particular gaps in recently developed areas and historically underinvested communities.
Climate resilience infrastructure requires significant investment to address wildfire risk, flooding potential, and extreme heat impacts that disproportionately affect vulnerable populations. Green infrastructure development offers opportunities to address environmental challenges while creating community amenities and economic opportunities.
Environmental Justice and Community Health
Air quality, green space access, and environmental equity analysis
Environmental justice concerns significantly affect community health outcomes, with air quality challenges rating 7.8 on impact severity scales and 9.1 on community priority measures. Industrial facilities, transportation corridors, and port activities create pollution burdens that disproportionately affect low-income communities and communities of color.
Green space access varies dramatically across county geography, with affluent neighborhoods averaging 8.2 acres of park space per 1,000 residents while underinvested areas provide only 1.4 acres per 1,000 residents. This disparity affects community health, property values, and quality of life measures that contribute to broader inequality patterns.
Water access and quality issues affect approximately 5.2% of county residents, with particular challenges in unincorporated areas and older housing stock. Lead contamination, aging infrastructure, and affordability challenges create barriers to safe water access that affect child development and community health.
Climate change adaptation requires comprehensive planning that addresses heat island effects, wildfire evacuation routes, and flooding mitigation while ensuring that adaptation measures do not increase displacement pressure on vulnerable communities.
Public Safety and Community Justice
Crime prevention, community policing, and restorative justice evaluation
Public safety approaches require community-centered strategies that address both immediate safety concerns and underlying social conditions that contribute to crime and violence. Current crime prevention programs receive 6.2 effectiveness ratings from community surveys, indicating significant room for improvement in program design and implementation.
Community policing initiatives show 5.8 effectiveness ratings, with community feedback emphasizing need for enhanced cultural competency, de-escalation training, and community engagement protocols. Youth programs demonstrate higher effectiveness at 7.1 ratings, suggesting that prevention-focused investments yield better community outcomes than enforcement-focused approaches.
Mental health crisis response capacity remains inadequate at 4.3 effectiveness rating, reflecting insufficient training, limited resources, and lack of coordination between public safety and mental health service systems. Crisis intervention teams serve only 28.7% of optimal coverage levels, creating gaps in emergency response for individuals experiencing mental health crises.
Restorative justice programs operate at only 15.9% of optimal funding levels despite community interest in alternatives to traditional criminal justice approaches. These programs show promise for addressing property crimes and community conflicts while reducing recidivism and building community connections.
Recommendations and Implementation Framework
Evidence-based priorities for policy intervention and resource allocation
Affordable housing production must increase to 30,000 units annually over five years to address current shortfall and projected population growth. This target requires streamlined approval processes, increased public investment through housing trust funds, and innovative financing mechanisms including community land trusts and social impact bonds.
Healthcare access expansion should prioritize community health center development in service desert areas, mobile clinic programs for rural and underserved communities, and telemedicine infrastructure that bridges geographic and transportation barriers. Mental health services require immediate capacity expansion through training programs, facility development, and integrated service delivery models.
Workforce development programs must align with projected employment growth in technology, healthcare, and skilled trades while providing comprehensive support including childcare, transportation, and financial assistance during training periods. English language learning integration with skills training offers opportunities to address multiple barriers simultaneously.
Infrastructure investments should prioritize public transportation expansion, broadband development in underserved areas, and community facility development that serves multiple functions including education, recreation, and social services. Green infrastructure development can address environmental challenges while creating community amenities and employment opportunities.
Environmental justice initiatives require comprehensive policy frameworks that address pollution reduction, green space development, and climate adaptation while ensuring that environmental improvements do not contribute to displacement of existing communities.